Call Us
90-216-380-5555

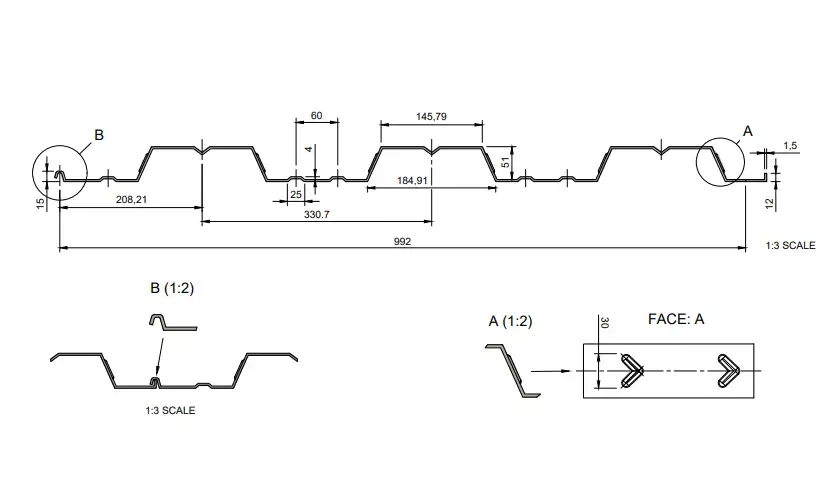
52/992 trapezoidal form for concrete substructure is one of the most suitable forms used to ensure integrity between concrete and steel in composite structures. It provides concrete savings and high durability. It can be produced in different thicknesses ranging from 0.70 to 1.50 mm from galvanized sheet. The net coating area is 992 mm. It can be cut in desired lengths. The maximum length is 15 meters.
What is a Composite Structure?
The most frequently used feature in Building Technologies is the ability to use different building materials together. The most important feature of the composite structure is the use of concrete and steel together. In the world's steel + concrete composite structures, various combinations of steel with high tension and flexibility feature and concrete with high compressive strength and corrosion resistance are used and applied. With the composite structure method, it is possible to combine the positive features of steel and concrete without any obstacles.
Stud Welding Applications in Structures
The Composite Structure Sector has an important place in the construction industry. It allows the building to be put into use earlier than the planned date, independent of weather conditions, thanks to its quick installation advantage. In areas where wide columns are not needed, it allows for more flexible use and more usage area. Since the beam sizes are lower than reinforced concrete, it allows for more floors to be made for the same building height due to the thinness of the slabs despite wide openings.
Advantages of Steel + Concrete Composite structures


SPREAD LOADS THAT 52/992 FORM TRAPEZOIDAL SHEETS CAN CARRY (Kg/m2)


| Joist Spacing (m) | Galvanized Sheet Thickness (mm) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 | |
| 1.20 | 1554 | 1768 | 1981 | 2192 | 2401 | 2609 | 2815 | 3019 | 3221 |
| 1.40 | 1142 | 1299 | 1455 | 1611 | 1764 | 1917 | 2068 | 2218 | 2367 |
| 1.60 | 874 | 995 | 1114 | 1233 | 1351 | 1468 | 1583 | 1698 | 1812 |
| 1.80 | 691 | 786 | 880 | 974 | 1067 | 1160 | 1251 | 1342 | 1432 |
| 2.00 | 559 | 637 | 713 | 789 | 864 | 939 | 1013 | 1087 | 1160 |
| 2.20 | 462 | 526 | 589 | 652 | 714 | 776 | 837 | 898 | 958 |
| 2.40 | 388 | 442 | 495 | 548 | 600 | 652 | 704 | 755 | 805 |
| 2.60 | 331 | 377 | 422 | 467 | 512 | 556 | 600 | 643 | 686 |
| 3.00 | 249 | 283 | 317 | 351 | 384 | 417 | 450 | 483 | 515 |
| Moment of Inertia (J:cm4/m) | 44.59 | 50.74 | 56.84 | 62.89 | 68.89 | 74.85 | 80.76 | 86.61 | 92.43 |
| Moment of Resistance (W:cm3/m) | 16.95 | 19.29 | 21.61 | 23.91 | 26.20 | 28.46 | 30.71 | 32.93 | 35.14 |
Safety Stress=1200 kg/cm2. Calculations are based on continuous beam shape.

